Table of Contents
Introduction
The sustentaculum tali is one of the most critical yet often overlooked structures in foot anatomy. Located on the calcaneus (heel bone), this bony protrusion plays a vital role in ensuring proper foot function. Specifically, it is crucial in supporting the foot arch, guiding the flexor hallucis longus (FHL) tendon, and maintaining ankle stability. This article will explore the anatomical features, functions, common injuries, and clinical significance of the sustentaculum tali.
Anatomical Features of the Sustentaculum Tali
The sustentaculum tali is a horizontal protrusion located on the medial (inner) surface of the calcaneus. This structure plays a critical role in supporting the foot arch and stabilizing the foot through its articulation with the talus bone. The sustentaculum tali also contains a groove through which the flexor hallucis longus tendon passes, serving a crucial function in directing this tendon (Olexa et al., 2000). With a concave articular surface, this structure is essential for maintaining the stability of the medial foot arch (Drayer-Verhagen, 1993).
Summary of the Anatomical Features of the Sustentaculum Tali
| Anatomical Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Situated on the medial surface of the calcaneus |
| Articular Surface | Concave, articulates with the talus |
| Function | Supports the foot arch and ensures stability |
Functions of the Sustentaculum Tali
The primary functions of the sustentaculum tali include:
- The primary functions of the sustentaculum tali include:
- Supporting the Medial Foot Arch: The foot arch is a complex structure that bears the body’s weight and facilitates movement. The sustentaculum tali plays a critical role in supporting this arch, maintaining its stability through its articulation with the talus bone (Al-Ashhab & Elgazzar, 2017).
- Guiding the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon: The FHL tendon passes beneath the sustentaculum tali, and this structure is essential in directing the tendon. This guidance is vital for the movement of the big toe and the overall balance of the foot and ankle (Marks et al., 1996).
- Maintaining Ankle Stability: The sustentaculum tali ensures stability between the foot and ankle by transmitting loads across the subtalar joint (the joint between the talus and calcaneus). This load transmission is crucial for the overall stability of the ankle joint (Drayer-Verhagen, 1993).
Read: Servant Leadership 101: Comprehensive Guide
Injuries to the Sustentaculum Tali
Injuries to the sustentaculum tali, while rare, can result in serious clinical consequences. These injuries typically occur due to high-energy trauma and are often accompanied by other foot and ankle injuries (Della Rocca et al., 2009). Common injuries to the sustentaculum tali include:
1. Fractures
Sustentaculum tali fractures are typically the result of falls or direct trauma. Such fractures can cause displacement of the articular surface between the talus and calcaneus, negatively impacting ankle stability. Sustentaculum tali fractures generally occur due to high-energy trauma, requiring surgical intervention. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a commonly used method for treating these injuries (Mahapatra & Chegu, 2023).
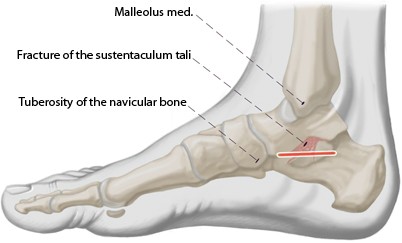
2. Malunion and Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
When fractures of the sustentaculum tali heal improperly or do not heal at all, complications such as tarsal tunnel syndrome can develop. This syndrome occurs when the bony protrusion of the sustentaculum tali presses on the tibial nerve, leading to chronic pain and restricted movement. Such cases often require surgical correction and nerve decompression (Myerson & Berger, 1995).
3. Instability of the Ankle Joint
Injury to the sustentaculum tali can destabilize the ankle joint. This can lead to long-term issues such as subtalar joint instability and arthritis (Drayer-Verhagen, 1993). Changes in the articular surface of the sustentaculum tali can restrict ankle mobility and cause pain.
| Type of Injury | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Fracture | Surgical intervention (ORIF) |
| Malunion | Surgical correction and nerve decompression |
| Ankle Instability | Physical therapy, surgical intervention (if necessary) |
Clinical Significance of the Sustentaculum Tali
The sustentaculum tali is a crucial structure for foot and ankle function. Injuries to this structure, if not treated properly, can lead to long-term restrictions in movement, chronic pain, and instability of the ankle joint. Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis and treatment of sustentaculum tali injuries are of utmost importance. For example, sustentaculum tali fractures often occur alongside other foot and ankle injuries, making them challenging to diagnose (Al-Ashhab & Elgazzar, 2017).
Preventing Injuries to the Sustentaculum Tali
To prevent injuries to the sustentaculum tali, consider the following recommendations:
- High-Risk Sports and Activities: Use appropriate protective equipment during sports and activities that may lead to high-energy trauma.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent long-term complications from sustentaculum tali injuries. Seek medical attention immediately if there are severe pain and hematoma around the ankle.
- Regular Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can accelerate the healing process and prevent long-term complications in the treatment of sustentaculum tali injuries.
Read: Is the Linea Aspera Anterior or Posterior?
Conclusion
The sustentaculum tali is a vital part of foot anatomy and holds a special place in orthopedic surgery due to its functional significance. This structure plays a critical role in supporting the foot arch, guiding the flexor hallucis longus tendon, and ensuring ankle stability. Although injuries to the sustentaculum tali are rare, they can result in serious clinical outcomes, and timely and accurate treatment is essential to prevent long-term complications.
REFERENCES
- Al-Ashhab, M., & Elgazzar, A. S. (2017). Treatment for displaced sustentaculum tali fractures. Foot, 35, 70-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foot.2017.12.002
- Della Rocca, G. D., Nork, S., Barei, D., Taitsman, L., & Benirschke, S. (2009). Fractures of the sustentaculum tali: Injury characteristics and surgical technique for reduction. Foot & Ankle International, 30(11), 1037-1041. https://doi.org/10.3113/FAI.2009.1037
- Drayer-Verhagen, F. (1993). Arthritis of the subtalar joint associated with sustentaculum tali facet configuration. Journal of Anatomy, 183(3), 631-634. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1259889/
- Mahapatra, P., & Chegu, M. (2023). Fracture of the sustentaculum tali: Features and surgical management for fracture reduction. International Journal of Life Science and Pharma Research, 13(2), 167-174. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369012423
- Marks, R. M., Antoniades, S., & Myerson, M. (1996). Injury to the sustentaculum tali. The Foot, 6(4), 182-187. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0958259296900206
- Martinou, V., Steiger, C., de Marco, G., Coulin, B., Vendeuvre, T., Morello, V., Habre, C., & Dayer, R. (2020). An incidental finding of an os sustentaculi with a concomitant talocalcaneal synchondrosis after a fracture of the internal malleolus in an 11-year-old child: A case report. Case Reports in Surgery, 3, 1-3. https://doi.org/10.15761/cris.1000131
- Myerson, M., & Berger, B. I. (1995). Nonunion of a fracture of the sustentaculum tali causing a tarsal tunnel syndrome: A case report. Foot & Ankle International, 16(11), 740-742. https://doi.org/10.1177/107110079501601113
- Olexa, T. A., Ebraheim, N. A., & Haman, S. P. (2000). The sustentaculum tali: Anatomic, radiographic, and surgical considerations. Foot & Ankle International, 21(5), 400-403. https://doi.org/10.1177/107110070002100507


